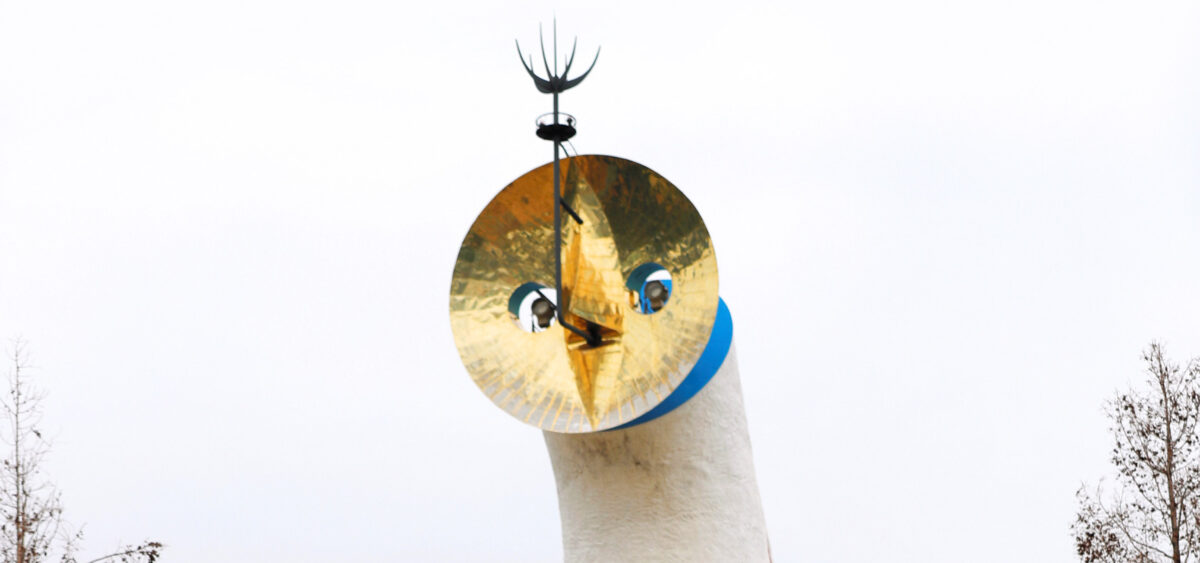
Some call him the only avant-garde artist in Japan. Although fascinated with Picasso, he didn’t reject tradition, but did the opposite. He discovered the ‘original Japan’ for his compatriots: prehistoric art. Who was the creator of the Tower of the Sun, Tarō Okamoto? “Art is explosion!” Tarō Okamoto shouted in a TV commercial after striking a bell of his own design. Originally he had created it for a Buddhist temple. Each of the horns on the spiky bell bowl produced a different sound. Nowadays nobody remembers anymore what Okamoto was advertising, but Japanese people still associate him with this catchphrase.
“Art is explosion!” In fact, few artists would agree with these words, not to mention living and creating in accordance with it. Constant explosions are very difficult and exhausting for an artist. But each time I encounter Okamoto’s art, I have a feeling that some kind of eruption has just taken place. And as a result, new forms of life appear, which cannot be inscribed into any type of standing biological classification. When I look at them, they also show interest and assess with their eyes. Pretty much all of Okamoto’s sculptures – even though it would be difficult to call them figures – have faces, masks, sometimes even more than one.
Preschool level?
It was because of Tarō Okamoto that I lost trust in my guide to Japan, the Japanologist Alex Kerr. In his Lost Japan, recently published in Polish, he ridicules Okamoto for sculpting like a